Data Tables
What is a data table?
A Data table is a collection of fields that comprise a common group.
For instance, a Companies data table would consist of a collection of basic information that would define each company, including Company Name, Company Address, Company Website, etc. Each item of information is referred to as a field, and all fields grouped together form a Companies data table. Click here to learn more about fields..
A data table is a collection of common fields, similar to how a spreadsheet is a collection of common columns.
In a spreadsheet titled Customers, there may be columns including First Name, Last Name, Email, and Gender. Each column refers to a basic item of information that describes a customer, and the collection of these columns defines the Customers spreadsheet. Similarly in Tadabase, a data table titled Customers would contain fields including First Name, Last Name, Email, and Gender, and the collection of these fields define the Customers data table.
Just as each row in a spreadsheet displays the collection of columns to form a single Customer record, a record in a Tadabase data table displays the collection of fields to form a single Customer record as well. In this way, records in a data table in Tadabase are similar to rows in a spreadsheet.
To sum the comparison of how Tadabase structures data similarly to spreadsheets, users can think of data tables as spreadsheets, fields as columns, and records as rows.
Data table vs. spreadsheet
Now that we've explained the similarities between a data table and a spreadsheet, let's explain how a data table and a spreadsheet differ and how these differences outline the very reasons why it is essential to use database applications over traditional spreadsheets.
Unlike spreadsheets, records within data tables can be connected to records within other data tables using a Connection Field. The ability to connect records reflects the core power of database applications and the primary reason why businesses seek database applications over traditional spreadsheets.
While Tadabase does an excellent job of storing your data, your data can't do much just sitting there in storage. Connections are what empowers you to take your data to the next level and what supercharges your data for faster and easier summarizing, tracking, calculating, reporting, and automation of all your business information.
Let's explore some of the key benefits of using connection fields to connect your records.
To automate and expedite adding new information
Using connection fields to connect records saves a significant amount of time when adding new information.
For instance, if you would like to track all your contacts and the companies they work for, you can create a Contacts data table and a Companies data table and use a connection field to connect the records within both data tables. Doing so would enable you to save a significant amount of time when adding new information because every time you add a new contact you can simply select the company that the new contact works while simultaneously viewing all that company's information.
With a traditional spreadsheet, you would have to re-enter the company's information from scratch every time you add new contact.
Using connection fields to connect records will save you invaluable time when adding new records and it can also reduce errors that come from repeated manual data re-entry.
To automate and expedite updating existing information
Using connection fields to connect records can also save a significant amount of time when editing existing information.
For instance, if you are tracking your Customers and Jobs with a traditional spreadsheet, this is how your Jobs spreadsheet may appear:
As you can see in the image above, there are three jobs, each with the same customer, "John Simonds". Each job record includes the Customer Name, Phone, and Email fields to display the customer's information. Say you need to edit Customer John Simond's name, you would need to edit his name throughout each job record that includes this customer's name field. This can quickly become tedious and repetitive and incur needless, manual errors.
With database applications and the use of connection fields, repetitive updating of individual fields becomes obsolete as you are able to update a field once which will automatically update any and all connected records that include that field.
To calculate and summarize information from a related data table
Using connection fields to connect records empowers you to calculate, summarize, and track related information from one single viewpoint at a glance.
For instance, say you have an Employee Time Tracking application with an Employees data table and a Time Sheet data table, and a connection field connecting these two data tables with each time sheet belonging to one employee. This connection field will empower you to track, calculate, and summarize information from one data table within another. For instance, from the Employees data table you can view values from the Time Sheet data table including each employee's total hours, average number of hours, and total weekly hours.
You can use the connection field to create any complex formula fields you need and summarize additional calculations such as employees' hours across custom pay periods and date ranges.
Additionally, you can use the connection field to automate critical calculations of your related data which can provide you with invaluable analytics and reporting functionality across all your values.
To summarize connected and related records on one details page
Using connection fields to connect records also enables you to track connected and related records on one details page.
For instance, say you have a Customers data table, a Jobs data table with a connection field to the Customers data table (each job belongs to a customer), and a Notes data table with a connection field to the Jobs data table (each note belongs to a job). Although the Notes data table is not connected to the Customers data table, it is related to the Customers data table via the Jobs data table.
Within a customer's details page, you can add the customer's connected jobs and related notes so that you are viewing all the customer's connected and related information on one page.
Click here to learn more about related records vs. connected records.
To automate changes in connected or related records
Using connection fields to connect records also empowers you to automate changes in related records, such as automatically updating and editing related records when forms are submitted.
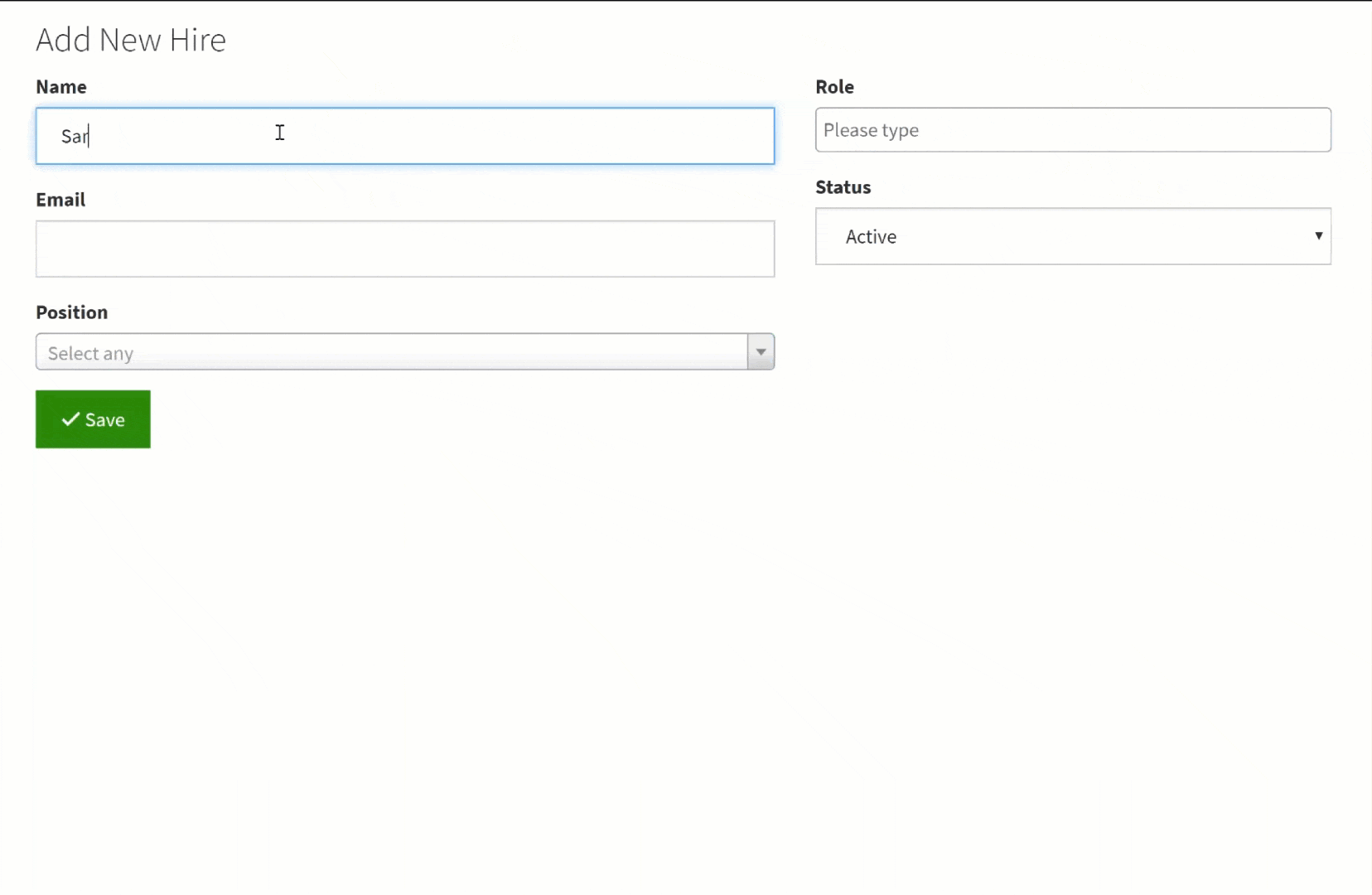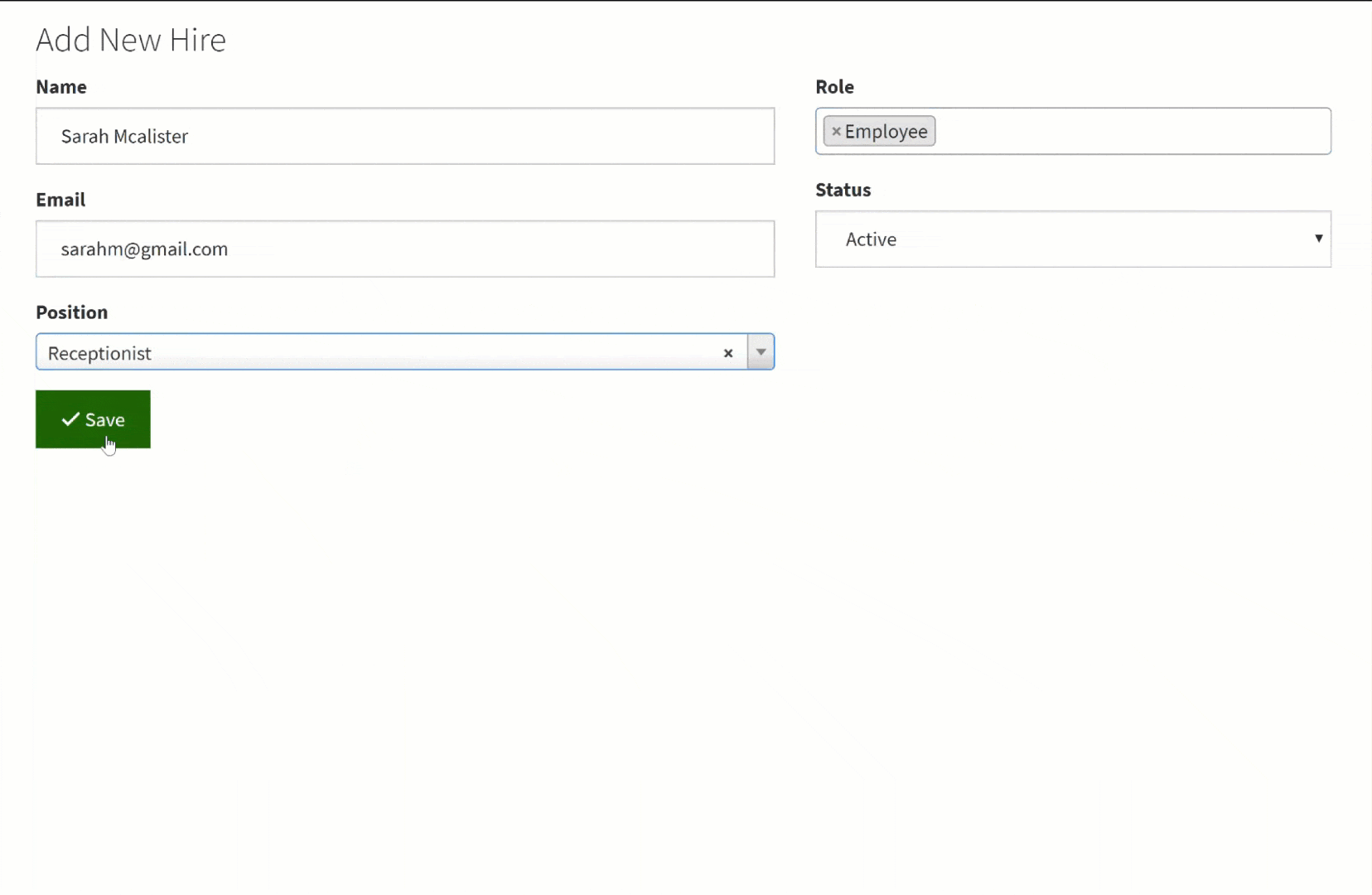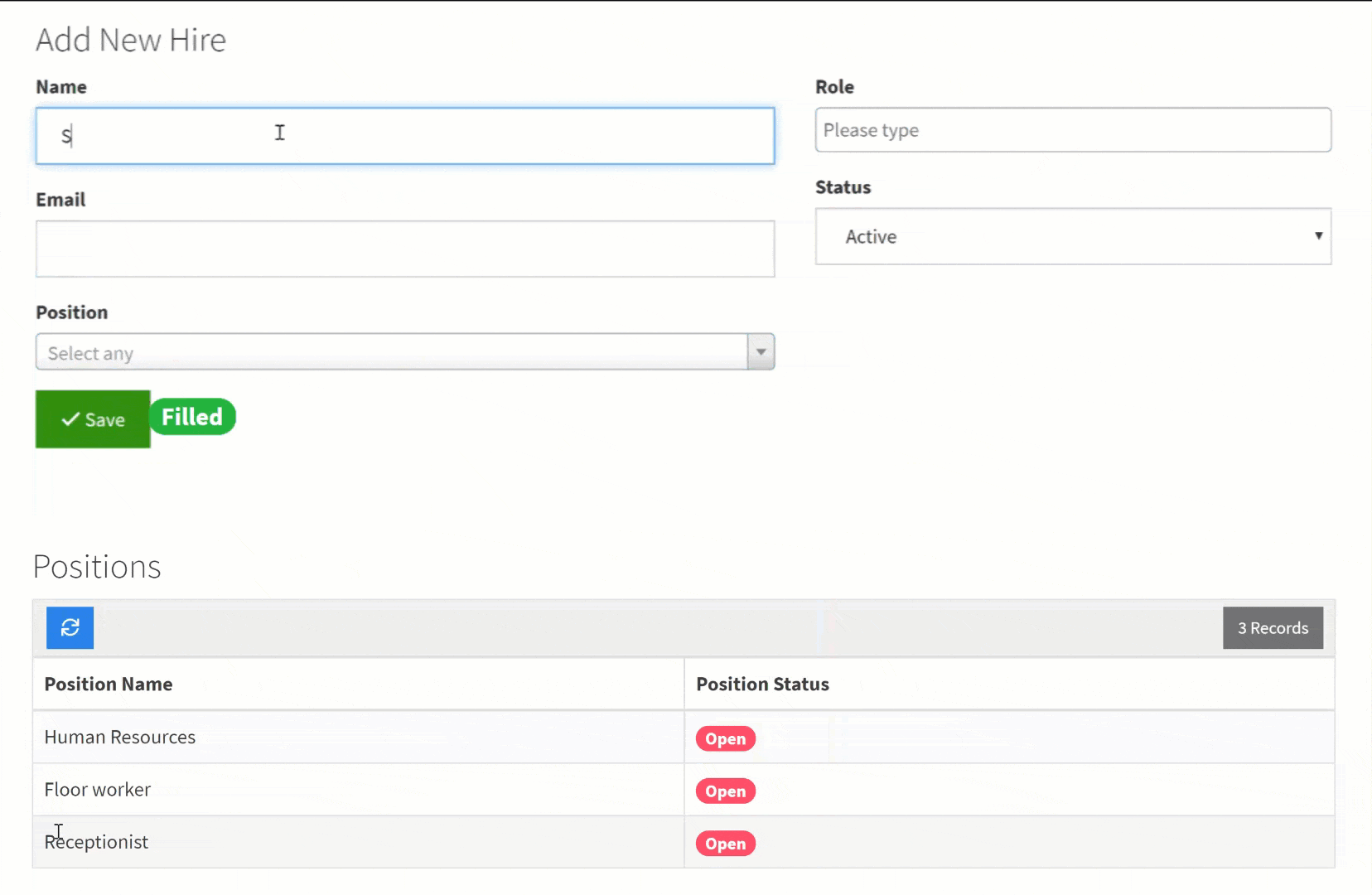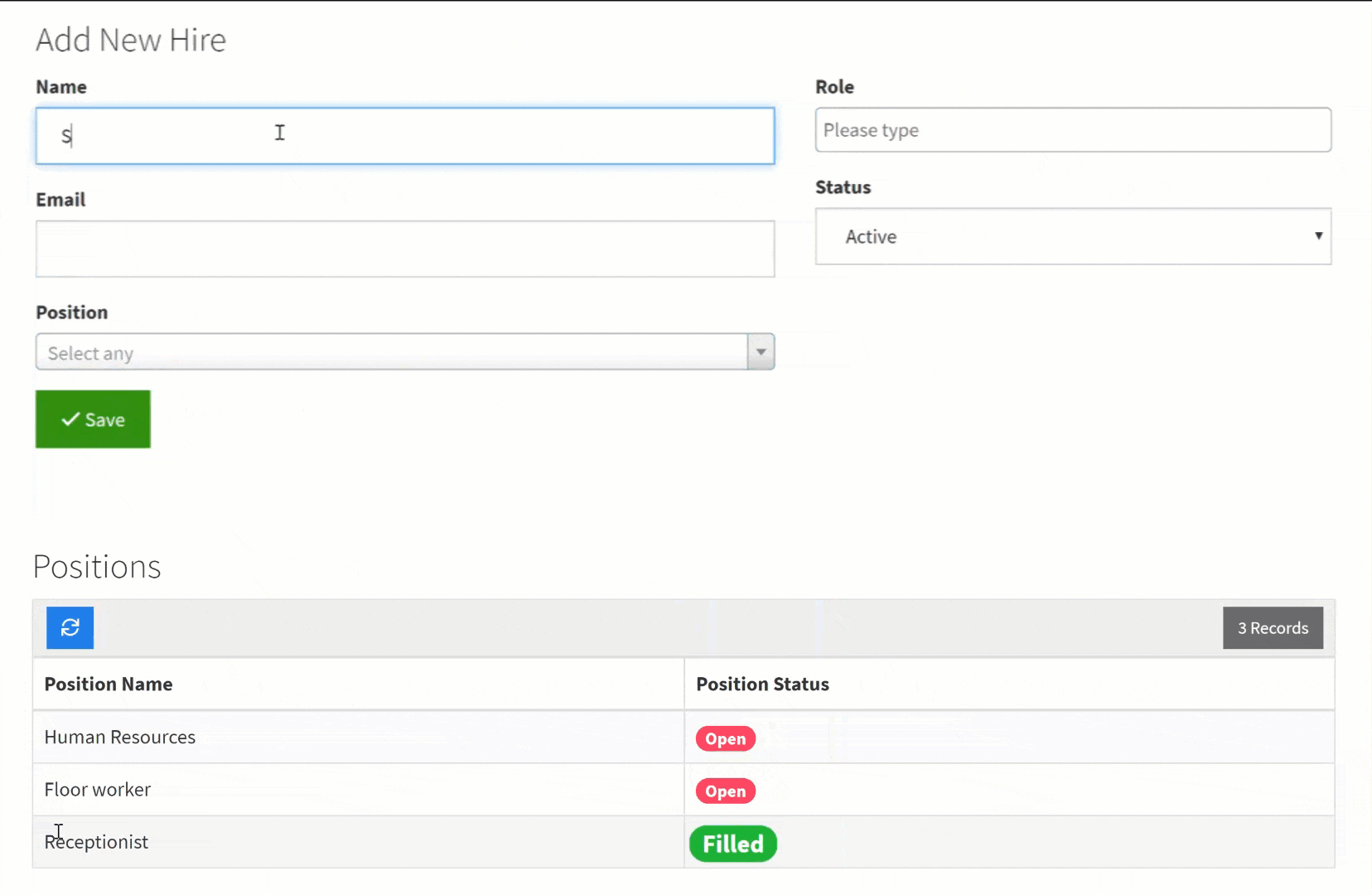
For instance, say you have open job positions and every time you hire a new employee and assign him/her to a position you can automatically update the position status from "open" to "filled". You can easily accomplish this with a connection field which will empower you to then create a record rule to automate this record update.
Click here to learn more about creating record rules to automate changes in connected or related records.
Click here to learn more about creating connections using connection fields.
Structuring data tables within your app
When creating your app, it is best to create a data table for each clustered type of data you would like to store. For instance, if you are creating a custom CRM app to track your customers, proposals, tasks, and notes, it would be best to create four separate data tables, one for each set of data.
Custom CRM Data Tables:
-
Customers data table
-
Proposals data table
-
Tasks data table
-
Notes data table
If you are creating a contact directory app to track your contacts, the companies each contact works for, and every time you communicate with each contact, you would create three separate data tables, one for each set of data.
Contact Directory Data Tables:
- Companies data table
- Contacts data table
- Communication Notes data table
Pluralizing your data tables
As each data table will display multiple individual records, it is best to title each data table in plural form rather than in singular form. For instance, a Customers data table will display multiple individual records of each customer while an Employees data table will display multiple individual records of each employee. Therefore, it is best to title data tables in plural formatting.
Adding parent data tables before child data tables
It is recommended to add data tables in the order of parent data table to child data table. The child data table refers to the data table that belongs to the parent data table, similar to how a child belongs to a parent. Similarly, the parent data table refers to the data table that is more likely to remain constant, or parent-like.
For instance, if you have a Contact Directory application with a Contacts data table to track your contacts and a Companies data table to track the companies each contact works for, the Contacts data table is the child data table that belongs to the Companies data table (each contact works for/belongs to a company). Similarly, the Companies data table is the parent data table that is more likely to remain constant (contacts will come and go from companies while companies are more likely to remain constant).
When adding data tables within the Data Builder, it is recommended to begin with adding the parent/most constant data table first. Therefore, in this Contact Directory example it would be recommended to first add the Companies data table and then add the Contacts data table. Adding data tables in this order will enable you to first add your companies, and when adding contacts have the ability to select connected companies from a drop-down list.
In the event that data tables were added to the Data Builder in the order of child to parent, such as first adding the Contacts data table and then adding the Companies data table, you can simply enable a form to pop up within your Contacts component on the live app in order to add new companies on the fly from the contacts component.
Click here to learn more about parent and child data tables and creating child-parent data table connections.
Default Data Tables
While you create the data tables that define your app's data structure, every new app comes with two default data tables that you will find whenever you create a new app.
When you create a new app and are directed to the Data Builder you will find two default data tables:
- Users data table
- Sample data table
Default users data table
The default users table is a pre-built data table you will use to add the data for the users whom you wish to log in to your app with role-based permissions.
For instance, if you are building a Project Management app you may wish to be the only user to login to your app to add and track projects, tasks, deadlines, team members, etc. In this case, you would create the following data tables for your Project Management app:
- Projects data table
- Tasks data table
- Team Member data table
and within the default Users data table you would only add the login and user role information for yourself, the only user who will be logging in to your app. You can assign yourself the role of Project Manager or App Admin or whatever other role you wish, and as the only user defined in the Users data table you will be the only user with permissions to login to your app.
Alternatively, you may wish to enable team members to login to your app as well to give them custom-defined team member permissions, such as the ability to update the status of their assigned projects or track their assigned tasks and deadlines.
In this case, you would create the following data tables for your Project Management app:
- Projects data table
- Tasks data table
In this case, rather than creating a Team Members data table you would add your Team Members data to the default Users data table in order to enable them to login with custom-defined Team Member role permissions.
To learn more about working with Users please click here.
Default sample data table
The second type of default data table that comes with each new app is the sample data table. To assist beginners with creating their first app, Tadabase provides a pre-built sample data table to demonstrate how Tadabase structures data with data tables, fields, and records.
This default sample data table can be deleted at any time by clicking on the Settings tab on the top data table menu and clicking Delete.
Creating New Data Tables
For your convenience, Tadabase offers two different methods for creating a new data table:
-
Create a new data table from scratch (recommended)
-
Import a CSV
From scratch
Creating a new data table from scratch is the most recommended method of adding a new data table because it offers the most flexibility and functionality to fully customize your data table around your exact data needs.
To create a data table from scratch, simply click the +Add Data Table button.
You will then be prompted to name your new data table. As a reminder, it is best to name your data table in plural formatting (Customers vs. Customer) as each data table will display multiple individual records of that data set.
You will have the expedited option to immediately add fields for this newly created data table by clicking on the Add Field button (expedited method), or you can click on the Create Table button to add fields on the next page (recommended due to the increased ease and flexibility this method provides for adding fields).
Each new data table will come with a default icon that will be displayed on its left within your app's list of data tables. This icon can be edited within the settings tab of each data table's navigation menu.
By importing CSV data
You can choose to add a new data table by importing data directly from an existing CSV file.
Uploading a CSV is a multi-step process and taking the necessary steps to verify that your CSV is formatted correctly will expedite the importing process drastically and ensure that your data is correctly imported.
To add a new data table by importing a CSV, click on the drop-down arrow to the right of the +Add Data Table button and select the +Add table from CSV option.
Once you select your CSV, you will be prompted to name your new data table.
You will then be prompted to browse for the CSV file you wish to upload to generate the new data table.
To auto-import your CSV data correctly, Tadabase will match your CSV header's columns with your new data table's fields. To do this, you will be prompted to answer whether your CSV file has a header row with names for each column and if yes, on which row are the column names located. Typically, CSV files do contain a header row with names for each column on Row 1 of the CSV file, so generally the response to this question will be "Yes, the headers are on row 1".
You will also be asked to select the type of delimiter your file contains. By definition, CSV (Comma Separated Values) files use commas as delimiters, and "comma" will generally be the response to this question. However, if your CSV file is configured with a different character delimiter you can define the correct delimiter here.
Once you have completed verifying this information regarding your CSV, you can click Upload.
You will then have the opportunity to confirm your CSV columns' names as you would like them to be transferred into fields within your new data table. If your CSV file contains columns that you do not wish to include in your data table, this is where you can choose to exclude those columns. Lastly, you will also be prompted to assign each included column with a field type (text, number, date, link, etc.) so that Tadabase can correctly transfer your CSV columns into data table fields.
A. This is where your CSV column names can be altered to match your desired field names within your new data table.
B. This is where can choose to include or exclude CSV columns from being imported to your new data table.
C. This is where you can choose a field type from the drop-down field type menu that best defines your column/field. This step is highly significant in correctly importing your CSV into a Tadabase data table as each field type comes with its own purpose and functionality. For instance, using a date field will allow you to filter your data with complex date formulas and calendar component functionality whereas a basic number field will not.
Fields and field types will be defined in detail in the following section.
Once you have confirmed the names and field types of the CSV columns you wish to include, click Save and watch as your CSV data is instantly imported into your new Tadabase data table.
Data Table Settings
You can view or change the settings of each data table at any time by clicking on the Settings tab of the selected data table's navigation menu.
Within the Settings tab of the selected data table, you can view or change the following data table settings:
-
Table Name - refers to the data table's pluralized name. Data tables are named in plural formatting as they store multiple individual records of a data set. For instance, a Customers data table will store multiple records of individual customers.
-
Singular record name - refers to the name of each single record within the data table. For instance, a single record in a Customers data table is called a Customer.
-
Description - this is where you can enter a brief description defining this particular data table for your own reference. Data table descriptions will not display within your application and are for your own reference.
-
Icon - this is where you can choose an icon to identify the selected data table (optional). Each new data table comes with a default database icon, however it may be helpful to choose a unique icon for each data table within each data table's settings to more easily track data tables within your app's list of data tables.
- Default Display Field - this refers to the field that will be used at default when viewing this data table or when adding a new connection to this data table.
- Default Sort Field - This is the field used to sort by within a connections drop-down. For instance, if you have a Companies data table, you can sort companies in alphabetical order when displayed in a connection drop-down. To do this, you would set Company Name as the default display name, choose Company Name as the default sort field, and choose ASC (ascending) as the default sort field order.
- This setting will also be applied to the Data Source > Sort by setting when adding a new component. - Default Sort Field Order- this refers to the ASC (ascending) or DESC (descending) order in which the default sort field will be displayed in a drop-down menu.
In this article, we have discussed how data tables can be used to define your app's data structure within the Tadabase Data Builder. In the following article, we will discuss how fields are used to define your app's data structure in the Data Builder as well and how each field type can impact your data tables' functionality and power.



















We'd love to hear your feedback.