Adding Pipes
You can add Pipes via two different methods:
Let's discuss both of these ways to add Pipes to your app.
Installing existing pipes
Tadabase has a growing library of pre-built Pipes you can install and utilize in your app.
There are two types of pre-built Pipes you can install:
- Configurable Pipes
- Non-configurable Pipes
Configurable Pipes
Configurable Pipes are customizable pipes with which you have full ability to modify all aspects of each pipe. Most pre-built pipes are configurable.
Non-configurable Pipes
Non-configurable Pipes, like the Tadabase Utility Pipes, are pre-configured with specific functions and only the default values that are used in the pipe can be modified.
To install either Configurable or Non-configurable pre-built pipes, click on the Pipes tab on your app's left-side navigation menu > Install Pipes button to see the list of available pipes you can install in your app. Click the Install button for a specific pipe and you will see the newly installed pipe on the left pane.
Adding Custom Pipes
You can choose to create custom pipes for your own custom integrations that can communicate with an API.
Building custom pipes require general knowledge of HTTP/REST and is for advanced users only. Most settings are specific to each API and you would need to consult the API documentation for the integration you are looking to build.
Please note: Tadabase does not not offer support for building custom Pipes.
Please note: OAuth 2.0 is not supported when Adding Custom Pipes.
Pipe settings
General
Within the General tab, you can set a name and description for the pipe.
Checking enable debug mode allows you to view the pipe response in the console of the live app.
Each Pipe is broken into Global Settings and specific API Calls.
API Calls
API Calls are the core of how Pipes work. When configuring an API Call for a Pipe, there are several tabs you can utilize to customize all the settings and options that must be configured to ensure that the API Call will properly work.
Let's explore each tab within a New API Call edit page.
Overview
Within the Overview tab, you must set the Method for the API Call, which is the type of request this API should use.
Generally, the specific API you are using will dictate the method. However as a general rule, you can set one of the following methods:
- GET = Retrieve Data
- POST = Save New Data
- PUT/PATCH = Update existing data
- DELETE = Delete data
The URL endpoint/destination where you will access/update the data you need. Often, this URL needs to be dynamically generated, in which case you can use Parameters for the dynamic values.
For instance, the URL below requires the specific data (VIN) to be added into the URL. Therefore, you can add a custom parameter called "VIN" which you can then set in the Parameters tab.
http://api.carmd.com/v3.0/port?vin={VIN}
Keep in mind that the Parameter Names must match the Parameters in the request. In the above example, if you add a custom parameter called "VIN" in the URL, then the Parameter name MUST be "VIN" as well.
Parameters
Parameters are any values that will be dynamically assigned anywhere in the API Call request. You can set Parameters in the Parameters tab of a New API Call edit page.
For instance, if you are working with a Weather API, in order to properly retrieve the weather you would need to send the location for which you want the weather. In this case, the location is the Parameter.
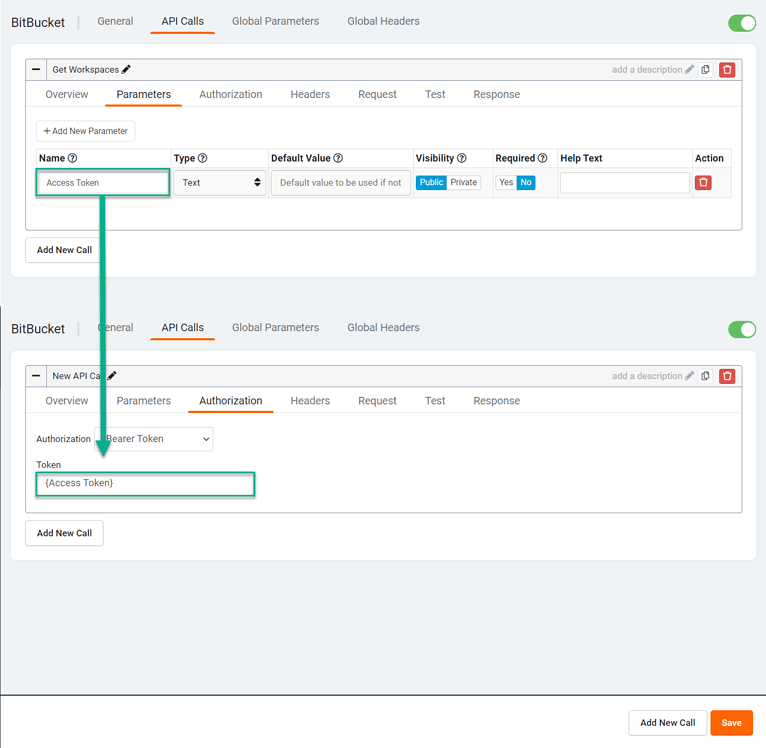
For example, you can create a Pipe parameter called “Access Token” and reference it in the Authorization tab by including the parameter name in curly brackets.
Authorization
Headers
If your API endpoint requires unique header values, you can add those within the Headers tab. Common header examples include: Content-Type and Authorization.
You must enter each header as a key-value pair. In the Key, enter the Header name as specified in the API documentation. In the Value, you can include a static value or a dynamic parameter by enclosing the parameter name in brackets.
In the example above, the headers will be sent as "Content-Type": "application/json", "X-Api-Key": "{x-api-key}", where {x-api-key} represents a dynamic parameter value.
See below for more information on Global Headers
Request
The Request tab is where you can pass data in the form of 'form-data' or 'raw' data.
Form-data must be entered as a key-value pair.
First, set the key value for the request. You can use dynamic parameter values by surrounding the parameter with curly braces. (For example: {Task Name} )
Then, set the default value for the request. You can use dynamic parameter values by surrounding the parameter with curly braces. (For example: {Task Name} )
Raw data
Enter the JSON structure of the request, according to the format in the API Documentation of the service you are trying to connect with.
You can add Parameters (that you created in the Parameters tab) directly into the request by clicking on the 'Add Parameter' dropdown menu.
Test
You can test this API call directly within the API Call Test tab. Using data from this test we can begin generating and mapping response data.
Response
The API must respond with either JSON or Raw values. You can map these responses to a specific name you choose and can then use it within your app.
Suppose we use the Weather API we can map each part of the return data to its own response key.
To know which values from the JSON response to assign you must first know the key.
Let's look at the following JSON response data. If we want to use the temperature value within our app, the key would be main.temp:
{
"main": {
"temp": 63.99,
"feels_like": 64.33,
"temp_min": 60.8,
"temp_max": 66.99,
"pressure": 1015,
"humidity": 82
}
}To map each of these we would use the parent key name with a dot (.) and the child key name.
If an array "[]" is returned we can access it by adding a ".0" or whatever index number we want to retrieve.
Suppose this response below:
{
"weather": [
{
"id": 800,
"main": "Clear",
"description": "clear sky",
"icon": "01d"
}
]
}As you can see the weather data is inside an array [] and therefore must be accessed using the index for each item.
Other response types:
If the response is only an array, you can access the responses with 0.key name.
[
{
"userId": 1,
"id": 1,
"title": "sunt aut facere repellat provident occaecati excepturi optio reprehenderit",
"body": "quia et suscipit\nsuscipit recusandae consequuntur expedita et cum\nreprehenderit molestiae ut ut quas totam\nnostrum rerum est autem sunt rem eveniet architecto"
},
{
"userId": 1,
"id": 2,
"title": "qui est esse",
"body": "est rerum tempore vitae\nsequi sint nihil reprehenderit dolor beatae ea dolores neque\nfugiat blanditiis voluptate porro vel nihil molestiae ut reiciendis\nqui aperiam non debitis possimus qui neque nisi nulla"
},
{
"userId": 1,
"id": 3,
"title": "ea molestias quasi exercitationem repellat qui ipsa sit aut",
"body": "et iusto sed quo iure\nvoluptatem occaecati omnis eligendi aut ad\nvoluptatem doloribus vel accusantium quis pariatur\nmolestiae porro eius odio et labore et velit aut"
}
]In this example, 0.userId would be the first record's user ID, 1.title would be the second record's title and so forth. 
Global Parameters
Global Parameters are the parameters that are applied to all of the individual API Calls.
Global Headers
Headers can also be added globally in the Global Headers tab. These headers would be applied to all of the individual API Calls.

















We'd love to hear your feedback.