Scheduled Tasks
The ability to automate your everyday business tasks is one of the most essential features of database applications. With automated tasks, you can trigger automated workflows to run upon custom-defined conditions at scheduled times or on-demand, automating your daily business processes and eliminating tedious, repetitive labor and manual error.
What are tasks?
Tasks refer to a custom-defined set of actions with conditions that you can trigger to run automatically on a custom schedule or on-demand.
Examples of tasks that you can automate include:
- Sending an automated email on the first of each month to all your active customers with their total balance due
- Sending automatic alerts to employees with outstanding tasks reminding them of their upcoming deadlines
- Sending an automated email to the respective manufacturer when a product reaches a custom-defined minimum inventory
- Generating PDF reports weekly for management
- Updating record statuses based on date conditions
- Creating connected records at specified intervals
How tasks are processed
Each task is associated with a specific data table. When creating a new task, it is important to first correctly determine within which data table you will create the task. In general, you want to create the task within the data table that you want the task to loop through.
Example: Say you have a rental management business and you want to create a new task to automatically generate a new invoice on the 23rd of each month for each of your active leases.
Question: When creating this task, would you create the task within the Invoices data table or within the Leases data table?
Answer: You would create the task within the Leases data table. This is because you want to create the task within the data table that you want the task to loop through, and even though the task is to create a new invoice, the task will look through all the records within the Leases data table to find those that match the conditions of your task and run your desired action (task) upon those records.
Another easy way to determine within which data table you should create the task is by noting the data table that follows the term "for each". For instance, your task will create a new invoice for each active lease.
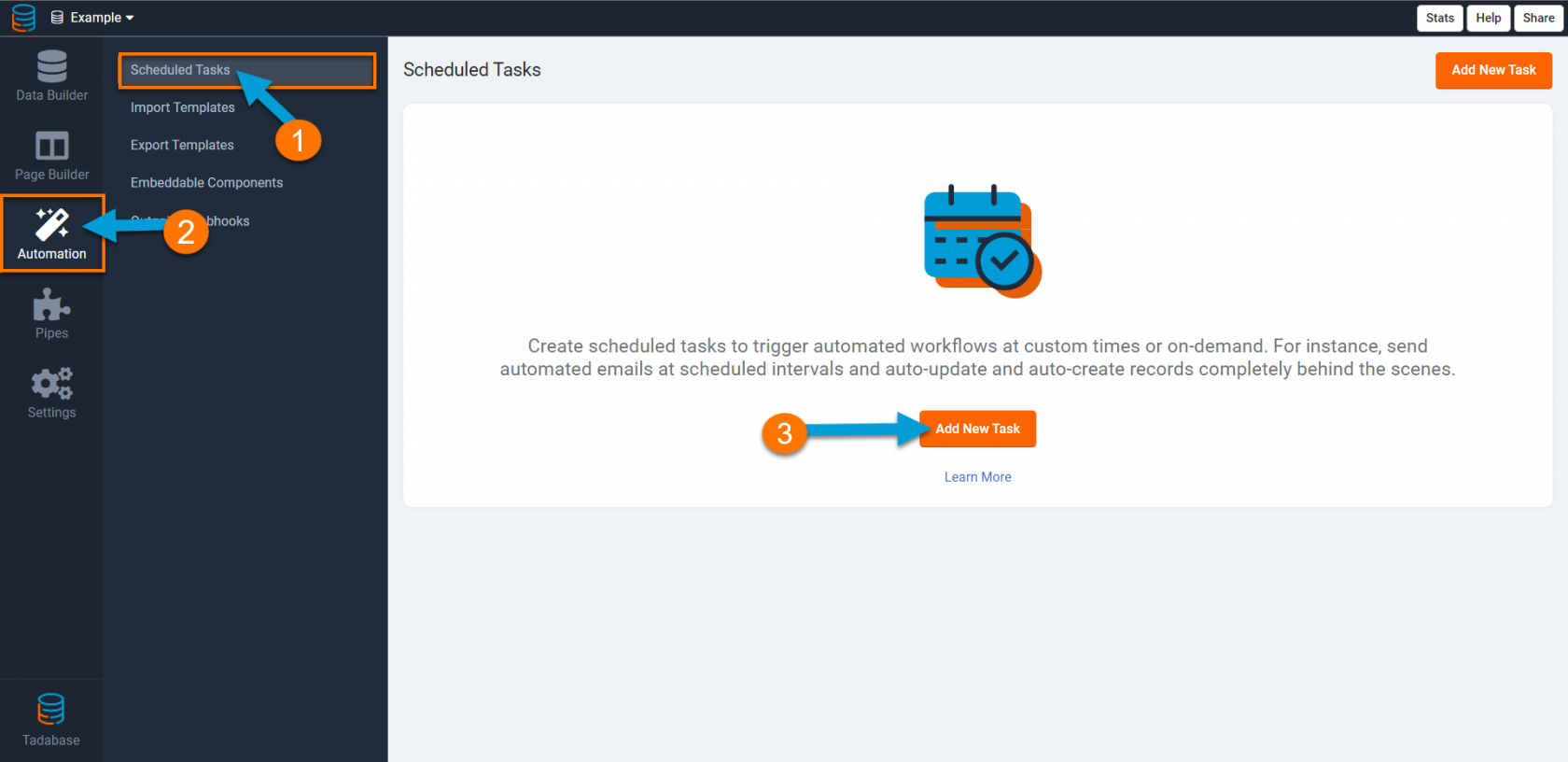
Creating a Task
To create a new task, select the Automation tab, click Scheduled Tasks, and then click on the Create a New Scheduled Task button.
Creating a task consists of several main components:
- General settings (name, table, schedule)
- Choose the action(s)
- Choose the conditions
- Set the field values
- Post-action options (optional)
Let's walk through each of these components below.
1. General Settings
First, define the basic settings for your task:
Task Name and Data Table
- Task Name: Give your task a descriptive name that explains what it does
- Data Table: Select which data table the task will operate on
- Task Description (optional): Add notes about what this task does for documentation purposes
Trigger Mode
Choose how the task should be triggered:
- On Schedule: Task runs automatically at specified intervals
- On Demand: Task only runs when manually triggered or called via API
Schedule Configuration
If you selected "On Schedule", configure when and how often your task should run:
Basic Scheduling Options:
- Every Minute: Runs every minute (Enterprise plans only)
- Hourly: Runs once per hour (Enterprise plans only)
- Daily: Runs once per day at a specified time
- Weekly: Runs once per week on a specified day and time
- Monthly: Runs once per month on a specified date and time
- Quarterly: Runs every three months
For each frequency, you'll also set:
- Start Date: When the task should begin running
- Time: What time of day the task should run (based on your app's timezone)
Important: The date and time this task will run is based on the timezone you have configured in your app settings. If your app has the default timezone of UTC and you set a task to run at 12:00 AM daily, it will run at 12:00 AM UTC. Changing your timezone will not impact when existing tasks run until you re-save each task.
Advanced Scheduling (RRule)
For more complex scheduling patterns, you can use the Advanced Schedule option (available on select plans). This allows you to:
- Run tasks on specific days of the week (e.g., every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday)
- Set custom intervals (e.g., every 2 weeks, every 5 days)
- Define complex recurring patterns using RFC 5545 recurrence rules
- View a human-readable description of your schedule
Example: "Every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday at 9:00 AM"
Tip: Advanced scheduling uses the RFC 5545 standard (RRule format) which provides powerful flexibility for complex scheduling needs. The interface will show you a plain-English description of your schedule as you configure it.
2. Choose an Action
Tasks can perform multiple types of actions. You can even configure multiple actions within a single task (multi-action tasks).
Available action types:
- Update this record
- Update connected records
- Insert connected records
- Insert new records
- Send email
- Send Text/SMS
- Generate PDF
Please Note: Not all actions are available in all scenarios. Certain actions such as Update connected records or Insert connected records are only available if there are specific connection fields in your data table.
Let's explore each action type:
1. Update this record
Update this record will cycle through all records in the data table and update specific fields to values that you have predefined.
Task Example: Every day at 8:00 AM, find each record with a balance higher than 0 and set status to "Past Due"
2. Update connected records
Update connected records will look through all records in the data table and for each record that matches your task conditions, will update all the connected records of a related table to predefined values.
Task Example: Every day at 5:00 AM, look through all bills that are overdue and set each connected customer's status to "Inactive"
3. Insert connected records
Insert connected records will create a new record in a connected table for each record in this data table that matches your conditions.
Task Example: On the 23rd of each month, create a new invoice record for each lease with a status of "Active"
4. Insert new records
Insert new records will create one or more new records that are not necessarily connected to records in this data table.
Task Example: Every Monday at midnight, insert a new record in the logs data table with a summary of all current leases
5. Send Email
Send Email will send an email for each record in the database that matches your custom-defined task conditions.
Task Example: Send a daily email at 7:00 AM to each customer who has an appointment scheduled for that day
6. Send Text/SMS
Send Text/SMS will send a text message for each record in the database that matches your custom-defined task conditions.
Task Example: Send a daily text message to each customer that has a job scheduled and has opted into SMS notifications
7. Generate PDF
Generate PDF will create PDF documents based on your predefined PDF templates for records matching your conditions.
Task Example: On the last day of each month, generate an invoice PDF for each completed project
Note: PDF generation in scheduled tasks requires a plan that includes the "allow_pdf_scheduled_task" feature.
Multi-Action Tasks
You can add multiple actions to a single task. For example, you might want to update a record AND send an email in the same task execution.
Example: Create a task that:
- Updates customer status to "Inactive" when payment is 30 days overdue
- Sends an email notification to the customer
- Sends an email notification to your billing team
Task action example
Now that we have identified each action type, let's look at a sample task action. As you can see in the image below, this sample task has the action of Inserting a connected record of a bill for each lease whenever the lease status is Active:

3. Choose Conditions
You can attach conditions to task actions to filter which records your task should process. For instance, "when the status is active":

You can add multiple conditions that work together using AND/OR logic. For instance:
- "Status is Active" AND "Created At is during the last 30 days"
- "Balance is greater than 0" OR "Status is Past Due"
To add additional conditions, click on the + icon next to existing conditions.
Tip: Use conditions to ensure your task only processes relevant records. This improves performance and prevents unintended changes to your data.
4. Set Field Values
For this step, you must specify the fields and field values to be used when the task runs.
For instance, if your task action is Send Email, you will need to set:
- To Email Address: Which field contains the recipient's email (or enter a specific email)
- Subject: The email subject line (can include merge fields)
- Message Body: The email content (can include merge fields from your data)
As another example, let's use the same example with inserting a connected invoice record:
Please Note: When setting values, the available options depend on the field type and the structure of your data table. You can use static values or dynamic values from the current record being processed.
5. Post-Action Options
After your task completes its main actions, you can configure additional post-action behaviors:
Email Notifications
Enable email notifications to receive an email when the task completes:
- Toggle on "Send email notification"
- Enter recipient email addresses (comma-separated for multiple recipients)
- The email will include task execution summary (success/failure, records processed)
Webhook Triggers
Configure webhook callbacks to notify external systems when your task runs:
- Webhook URL: The endpoint to POST task results to
- Success Callback URL (optional): A different URL for successful completions
- The webhook payload includes task status, records processed, and execution time
Tip: Use webhooks to integrate scheduled tasks with external systems, trigger additional workflows, or log task execution in third-party services.
Running Tasks
Tasks can be triggered via four different methods:
1. Scheduled Automatic Execution
With scheduled tasks, your tasks run automatically at custom-defined intervals on a recurring basis based on the schedule you configured.
How it works:
- The system checks every minute for tasks that are due to run
- When a task's scheduled time arrives, it's added to the task queue
- The task processes records according to your conditions and actions
- Results are logged in the task history
- The next run time is automatically calculated based on your schedule
Note: Tasks are processed in a queue system, which means they run asynchronously in the background without blocking other operations in your app.
2. On Demand (Manual Execution)
You can run tasks on demand at any time, which is useful for testing or one-time executions.
To run a task manually:
- Open the task in the builder
- Click the Run Task button at the top right of the task edit page
- The task will execute immediately

Tasks must first be saved before they can be run. Making any changes to a task will disable the Run Task button until you save your changes.
3. Via Task Manager Component
You can add the Task Manager Component to your pages, enabling end users to view, monitor, and trigger tasks directly from your live application. This is one of the most powerful ways to make tasks accessible to your users without giving them builder access.

What is the Task Manager Component?
The Task Manager Component is a System Component that provides a comprehensive interface for end users to interact with tasks. Unlike a simple button, the Task Manager Component offers a full task management experience including:
- View All Tasks: Display a list of all available tasks with details like name, description, schedule, and status
- Search and Filter: Users can search for tasks by name or filter by data table and folder
- Task Details: View comprehensive information about each task including configuration and schedule
- Execution History: Monitor past task runs, view success/failure status, and see record counts
- Trigger Tasks: Run on-demand tasks or manually trigger scheduled tasks with a single click
- Real-time Status: See which tasks are currently running and monitor their progress
Benefits of Using the Task Manager Component
- Self-Service Operations: Allows users to run tasks without accessing the builder
- Transparency: Users can see when tasks last ran and view execution history
- Permission Control: Fine-grained control over who can view and trigger specific tasks
- User-Friendly Interface: Organized, searchable interface designed for end users
- Workflow Integration: Enables task execution within user workflows and processes
- Monitoring: Users can track task execution status and troubleshoot issues
Common Use Cases
The Task Manager Component is ideal for scenarios where users need to:
- Generate reports on demand
- Trigger batch data processing operations
- Send notifications to groups of users
- Export data files
- Run maintenance or cleanup tasks
- Initiate automated workflows
Learn More: For detailed information about adding and configuring the Task Manager Component, including settings, permissions, and best practices, see the Task Manager Component documentation.
4. Via API
Tasks can be triggered programmatically using the Tadabase REST API.
API Endpoint:
POST /api/v1/tasks/run/{taskId}Use cases:
- Integrate task execution with external systems
- Trigger tasks from webhooks or third-party services
- Build custom automation workflows
- Execute tasks based on events outside of Tadabase
Note: API task execution requires a plan that includes the "allow_task_in_api" feature.
Monitoring and Managing Tasks
Task History and Logs
Within each task, you can view comprehensive execution history including:
- Start Time: When the task began executing
- End Time: When the task completed
- Status: Success or Failed
- Records Processed: How many records were affected
- Task Type: The action that was performed
- Trigger Source: Schedule, API, Manual, or Component
- Error Details: If the task failed, what went wrong
To view task history, click on the History tab inside the task editor.

Task Queue Status
View the current status of running tasks in the Task Queue tab:
- See which tasks are currently executing
- Monitor progress for long-running tasks
- View total records and records completed
- Terminate stuck or problematic tasks if needed
Organizing Tasks with Folders
As you create more tasks, you can organize them using folders:
- Create folders to group related tasks
- Drag and drop tasks into folders
- Filter views by folder
- Improve navigation and task management
Enabling and Disabling Tasks
You can temporarily disable a task without deleting it:
- Use the toggle switch at the top of the task editor
- Disabled tasks will not run on their schedule
- The task configuration is preserved and can be re-enabled anytime
- Useful for temporarily pausing tasks during maintenance or testing
Task Allowances and Plan Limits
Please note that not all Tadabase plans include the ability to automate tasks. Check your subscriptions page or the Tadabase pricing page to see if your plan includes tasks.
Execution Time Limits
Each plan has unique limitations on how long each task can run:
- Plus: 5 Minutes (approximately 100,000 minor record updates, or 5,000 complex updates)
- Pro: 10 Minutes
- Premium: 15 Minutes
- Bronze: 20 Minutes
- Enterprise: 1 Hour
Frequency Limits
The shortest interval available depends on your plan:
- Standard Plans (Plus, Pro, Premium, Bronze): Daily minimum
- Enterprise Plans: Additional options including:
- Hourly
- Every Minute
- Custom intervals (as low as every 5 minutes with advanced scheduling)
Feature Restrictions by Plan
Certain task features are restricted to specific plans:
- Advanced Scheduling (RRule): Available on select higher-tier plans
- PDF Generation in Tasks: Requires plans with PDF task support
- API Task Execution: Requires plans with API task support
- Multi-Action Tasks: Number of actions per task may be limited by plan
Best Practices for Scheduled Tasks
Testing Your Tasks
- Start with a small test: Use conditions to limit the task to a small subset of records first
- Use On Demand testing: Run the task manually before scheduling it
- Check the history: Review execution logs to ensure the task behaves as expected
- Monitor the first scheduled runs: Watch the task closely during its first few automatic executions
Performance Tips
- Use specific conditions: Don't process more records than necessary
- Schedule during off-peak hours: Run resource-intensive tasks when user activity is low
- Break up large tasks: If a task times out, consider splitting it into multiple smaller tasks
- Use indexes: Ensure fields used in conditions have appropriate database indexes
Reliability Tips
- Set up email notifications: Get alerted if tasks fail
- Review task history regularly: Check for failures or anomalies
- Document your tasks: Use the description field to explain what each task does
- Organize with folders: Keep related tasks grouped for easier management
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Task Not Running
If your task isn't running as expected:
- Verify the task is Enabled (toggle switch is on)
- Check that the start date hasn't been set in the future
- Confirm your plan includes the frequency you selected
- Review the task conditions - no records may match your filters
- Check if you've reached your plan's task limit
Task Timing Out
If your task is timing out before completion:
- Reduce the number of records being processed (add more specific conditions)
- Simplify the actions being performed
- Consider upgrading to a plan with longer execution time limits
- Break the task into multiple smaller tasks that run sequentially
Task Failing
If your task shows as "Failed" in history:
- Check the error message in the task history log
- Verify all required fields have values
- Ensure email addresses are valid (for email tasks)
- Confirm connection fields are properly configured (for connected record tasks)
- Test the task manually to reproduce and debug the error


We'd love to hear your feedback.